Fixed Asset Depreciation Utility
As your fixed assets age, you need to track the depreciation of them for your reports. The Fixed Asset Depreciation Utility calculates the reduction in value of an asset due to normal usage, wear and tear, new technology, or unfavorable market conditions. Assets such as plant materials and machinery, buildings, vehicles, and other assets which are expected to last more than one year but not for infinity are subject to depreciation. The Fixed Asset Depreciation feature gives you a way to record the depreciation of such assets.
Depreciation can be calculated many ways. Straight-line depreciation is the simplest, dividing the fixed asset’s cost by the number of accounting periods it is expected to last. Other methods might yield greater depreciation in early accounting periods or take into account the salvage or scrap value of the fixed asset after it is fully depreciated.
Please contact your aftermarket sales representative to enable this feature.
Non-Standard GL users who use this feature will see non-standard cycles as opposed to cycles shown for Standard GL users. These Non-Standard GL cycles are defined in Maintenance>Database>Parameters>General Ledger tab. Click here to learn more about Non-Standard GL.
Using Fixed Asset Depreciation
The steps on how to setup Fixed Asset Depreciation are listed below.
To add a new fixed asset depreciation record:
1. From the Main Menu, choose General Ledger > Utilities > Fixed Asset Depreciation. The Fixed Asset Depreciation form displays.
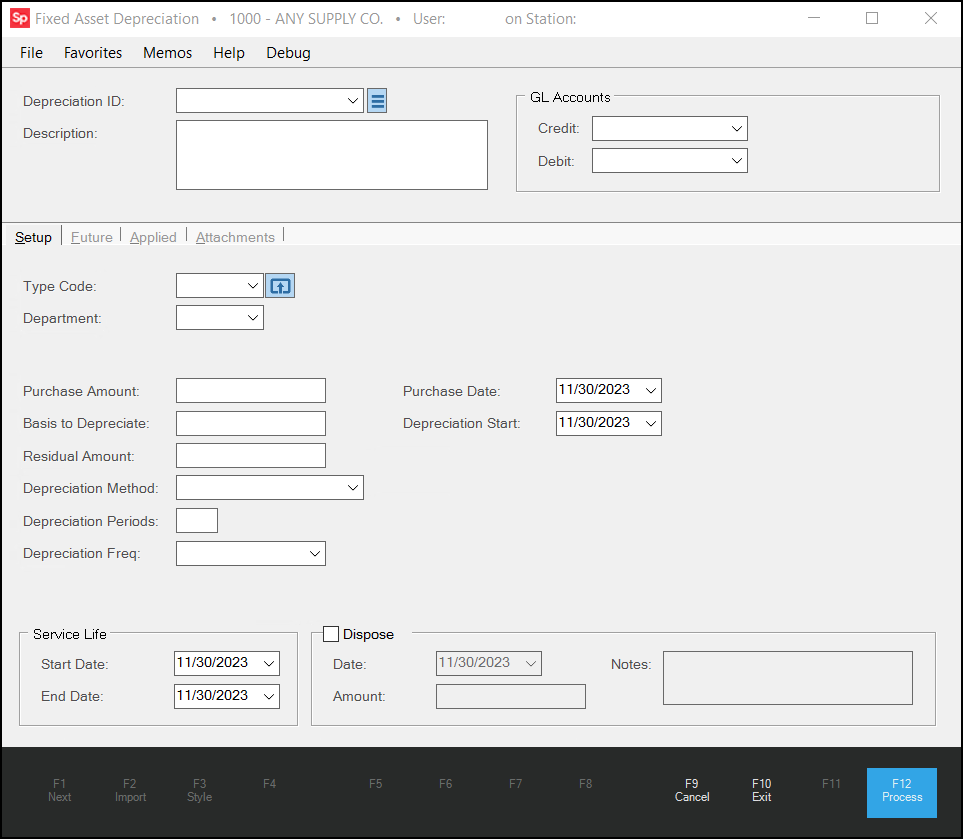
2. In the Depreciation ID field, enter a new Depreciation ID and enter a description for it in the Description field.
Note: If you discover that you created a depreciation record by mistake or you created a duplicate, you can delete it by selecting the Menu Marker  beside the Depreciation ID list and selecting Delete Schedule. You cannot delete a schedule that has existing journal records.
beside the Depreciation ID list and selecting Delete Schedule. You cannot delete a schedule that has existing journal records.
3. In the GL Accounts box, select the Credit and Debit GL Accounts you want to use to keep track of the asset depreciation record you are creating.
The Debit GL account is usually an expense account and is the offset to the credit reducing the asset value.
4. In the Setup tab, complete the following entries:
-
Type Code
The purpose of this entry is to identify the type of depreciation for the asset. This can be vehicles, equipment, property, etc.-
If this entry has been defined already, select the type from the list.
-
If not, click the Settings
 icon to display the Depreciation Type Code Maintenance box.
icon to display the Depreciation Type Code Maintenance box.
-
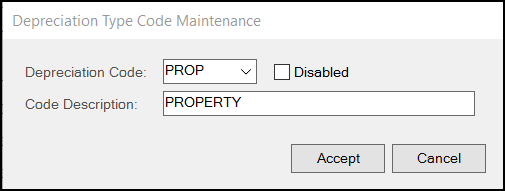
In the Depreciation Code field, enter the new type code and press Enter.
In the Code Description field, enter a description for the code type so other people can use it later and click Accept. When the Setup tab redisplays, choose the new Type code from the list.
-
Department
Select the department (branch) to which the asset is assigned. Departments are defined in the Base Department Codes section found in Maintenance > Database > Parameters > General Ledger. -
Purchase Amount
Enter the total purchase amount paid for the asset. The application uses this entry for reference only, not for calculations. -
Basis to Depreciate
Enter the amount of a fixed asset’s cost that can be depreciated over time. This amount is the acquisition cost of an asset, minus its estimated salvage value at the end of its useful life. -
Residual Amount
Enter the amount remaining after all other effects have been removed or otherwise accounted for. -
Depreciation Method
Choose from the following to define the appropriate depreciation method for this asset:-
Straight Line
Use this method to charge the same amount of depreciation to expense in every reporting period. This approach probably approximates the average usage pattern of most assets, and so is a reasonable way to match revenues to expenses. It is also the easiest depreciation method to calculate, which makes it by far the most used depreciation method. -
Declining Balance
Use this method to charge the bulk of the depreciable amount of the fixed asset to expense as soon as possible, with a rapidly declining amount being charged to expense in later periods. -
Double Declining Balance
Use this method to accelerate the depreciation, under which most of the depreciation associated with the fixed asset is recognized during the first few years of its useful life. -
Percentage
Use this method to express the annual depreciation as a fixed percentage of the book value at the beginning of the year. It is calculated by multiplying the book value at the beginning of each year with a fixed percentage. This method is also referred to as fixed percentage method of depreciation. -
Sum of Year
Use this method to accelerate the recognition of depreciation. Doing so means that most of the depreciation associated with an asset is recognized in the first few years of its useful life. -
Units
Use this depreciation method when the amount of depreciation charged to expense varies in direct proportion to the amount the use of the asset. A business may charge more depreciation in periods when the asset gets more use and less depreciation during periods when there is less use. This is the most accurate depreciation method, since it is linked to the actual wear and tear on assets. However, it also requires that someone track asset use, which means that its use is generally limited to more expensive assets. -
Manual
Use this method to calculate the depreciation as a percentage of the acquisition price. For manual depreciation, the percentages that you enter in the Percentage column on the Future tab do not have to add up to 100%. Together, the manual schedules and the posting intervals define the depreciation amount.
-
-
Depreciation Periods
Enter the number of periods used to calculate depreciation for this code type. -
Depreciation Frequency (Freq)
Indicates how frequently to calculate the depreciation for this code type. Options include: Monthly, Quarterly, Semi-Annually, Yearly, and Custom. When you choose Custom, the application assumes you are selecting the Manual depreciation method. -
Purchase Date
Choose the purchase date of this asset from the list. -
Depreciation Start
Choose the first date of the depreciation start for this asset from the list. -
Service Life Start Date
Choose a date that is equal to or later than the purchase date. -
Service Life End Date
The application chooses this date automatically based on the depreciation period and frequency you chose above. -
Dispose
Select this check box when you have disposed of the assets and enter the date, and the asset value at the time of disposal. No journals are created for asset disposal.
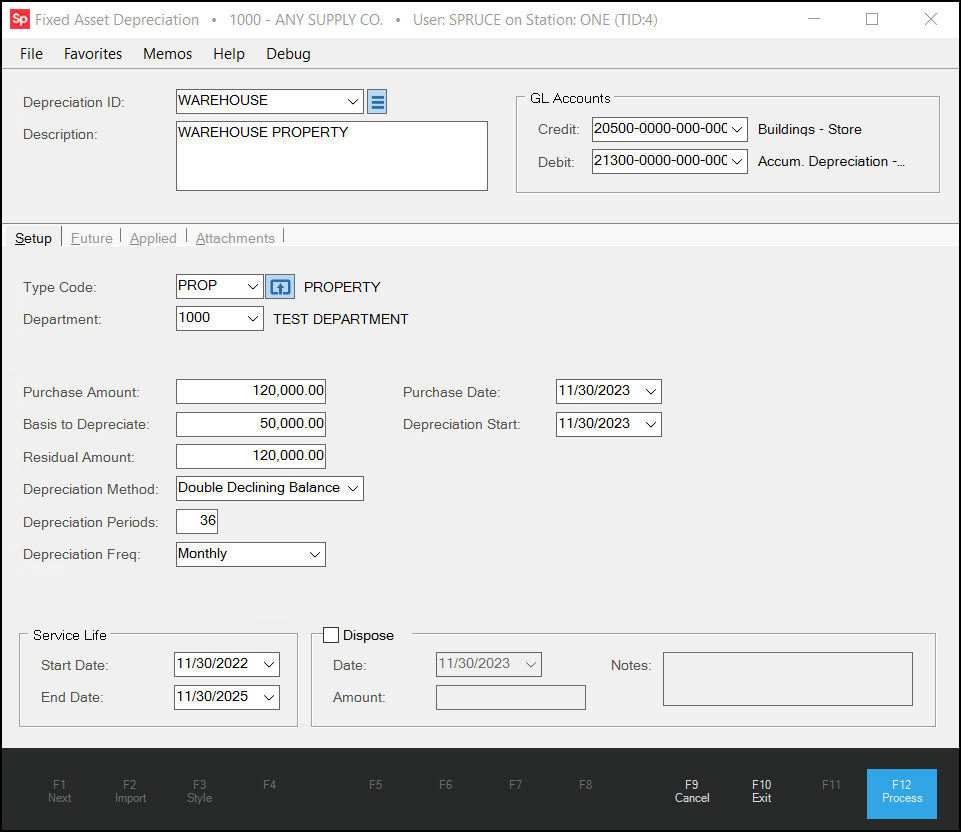
Fixed Assets Depreciation Form > Setup Tab
5. To save these settings, choose Process (F12).
6. To see the depreciation schedule based on your entries, return to the Fixed Asset Depreciation form and choose the same Depreciation ID again. The settings you entered display.
7. Click the Future tab.
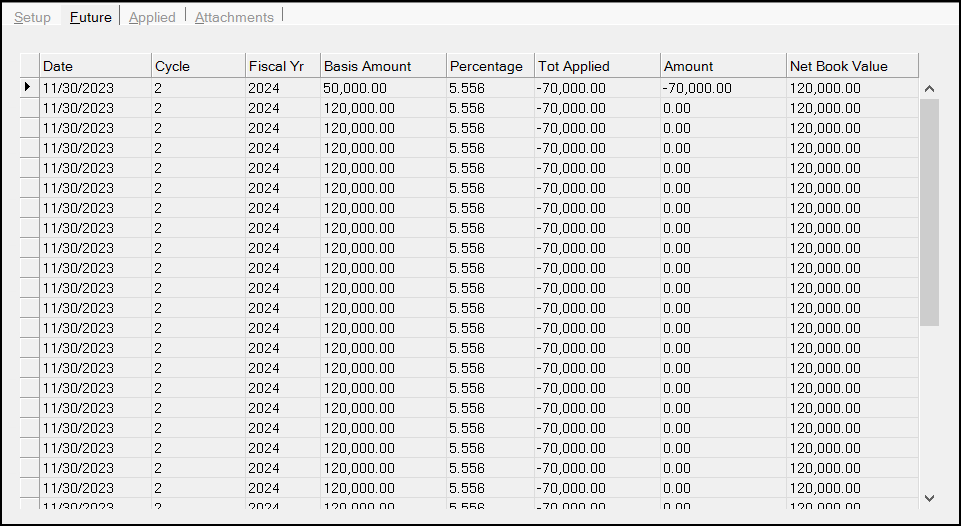
Fixed Assets Depreciation Form > Future Tab
This tab lists any depreciation schedule records still to be recorded in a GL Journal. The Net Book Value will never go below the defined Residual Amount defined on the Setup tab. You cannot edit entries in this tab.
8. Click the Applied tab to display the completed depreciation schedule records.
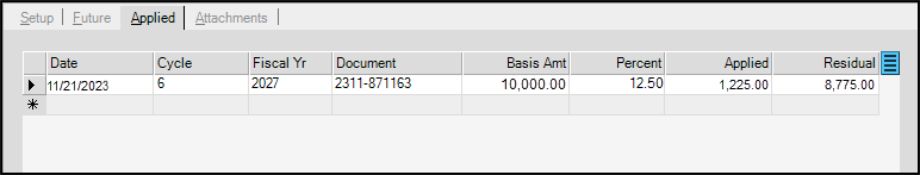
Fixed Assets Depreciation Form > Applied Tab
“Completed” means that a GL Journal document has been created for the depreciation period, and that your team has manually marked the depreciation as complete. You cannot edit entries in this tab.
9. Click the Attachments tab.
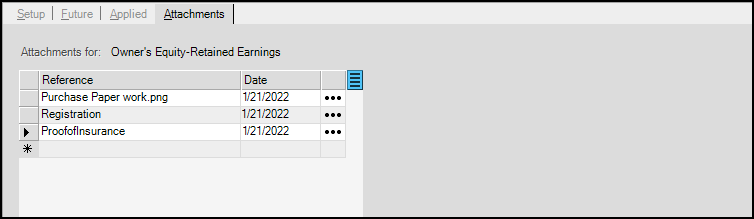
The Attachments tab is used to attach files and other types of information relevant to the asset. Attachments may be Windows-based files, website (URL) addresses, Map Links, or application document IDs. For more information on how to use the Attachment feature, click here.
Deleting Depreciation Records
If you discover that you created a depreciation record by mistake or you created a duplicate, you can delete it by selecting the Menu Marker ![]() beside the Depreciation ID list and selecting Delete Schedule. You cannot delete a schedule that has existing journal records.
beside the Depreciation ID list and selecting Delete Schedule. You cannot delete a schedule that has existing journal records.
See Also:
Fixed Asset Depreciation Examples