Parameters > Inventory Tab
Inventory parameters are used to set a number of preferences for managing your inventory in the application.
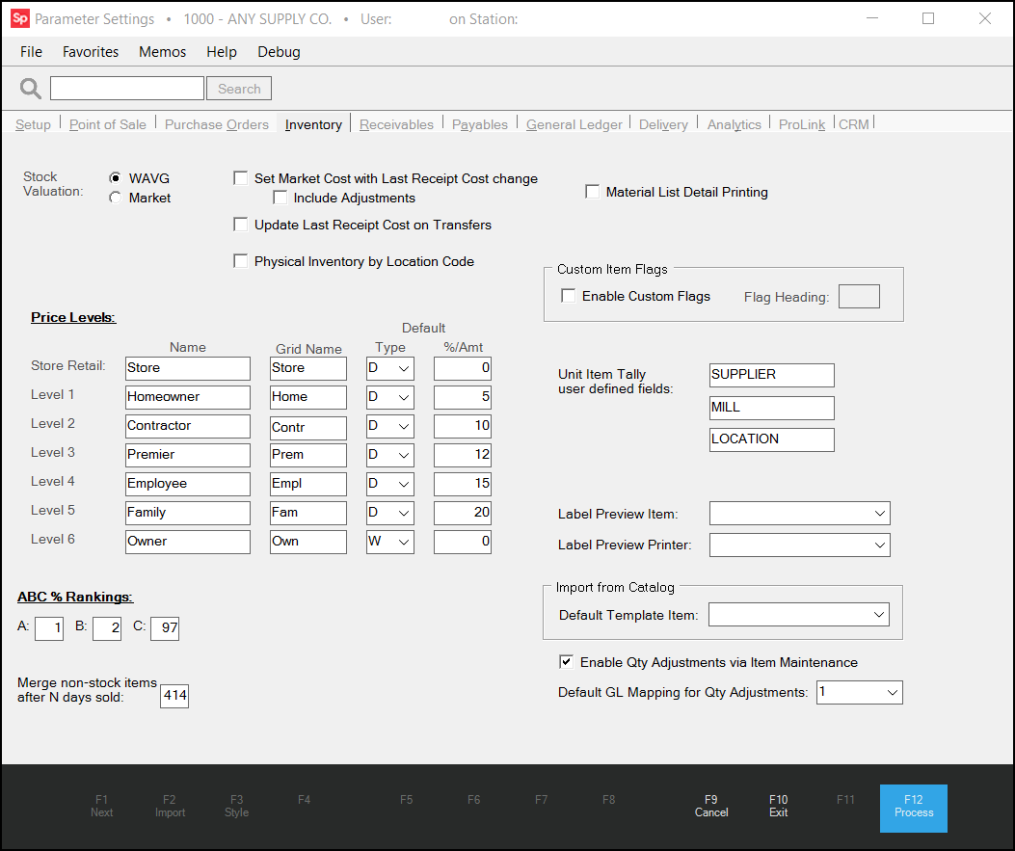
Stock Valuation Display
Use these radio buttons to select the cost method to use for display of monthly stock valuation records for inventory items. Choices include either WAVG (Weighted Average Cost) or Market Cost. The application maintains stock valuation records for items using both the Weighted Average and Current Market Costs when they are created. The Current Market Cost is a manually set cost, unless the Set Market Cost with Last Receipt Cost Change (see below) is also set. If the Set Market Cost with Last Receipt Cost Change check box is enabled, the application updates the item value each time the item is received into inventory. The selection of the Weighted Average Cost or Current Market Cost parameter, only alters the display of the item costs in the Item Maintenance and Inquiry forms when stock valuation is being displayed.
Set Market Cost with Last Receipt Cost Change
When this option is enabled (checked), the application updates the Market Cost for items each time the "Last Receipt" cost changes. In this case, the application retains previously entered market costs but only until the next change in the item's "last receipt" cost. From that point forward, both costs are updated and will match unless the market cost is modified in between receipts by a user. When this option is not enabled, you can set the item's Market Cost manually, which is intended to be a comparison cost reflecting the current market value of the item.
Include Adjustments
Check the "Include Adjustments" check box to include adjustments (such s freight, delivery costs, etc.) when updating the market cost of an item when the last receipt amount changes. Last Receipt will not include adjustments even if this parameter is checked.
Weighted Average cost-based items always include adjustments regardless of this parameter setting.
Caution: If you select this check box, but have not selected the "Set Market Cost with Last Receipt Cost Change" check box, the application assumes that this check box is enabled. As a result, the application will update the Market Cost of each item based on the last receipt amount changes (even if you have not enabled this parameter)!
Update Last Receipt Cost on Transfers
Transfers of inventory do not default to update the "last receipt" cost for items in the receiving branch's inventory file. Whether or not your company chooses to enable this option depends on the primary reasons for transfers. In the case of a "warehouse" branch (central purchasing location), it's probably best to update the last receipt cost after transfers to keep branch costs up-to-date, for example.
Last receipt cost will only be updated by transfers if this parameter is checked. The cost used for transfers is always the weighted average cost. This parameter just determines whether a transfer updates the item's "last receipt" cost for transfers as well as regular receipts.
In addition to the last receipt cost, the "last receipt date" is also updated by transfers, but only if this parameter is enabled (checked).
Physical Inventory by Location Code
If this setting is enabled (checked), the application replaces the default Group/Section column in the Enter Counts item grid with a Location column. By doing this, you can sort the grid based upon location code instead. To perform a permanent sort, a column matching the sort must exist in the grid.
Material List Detail Printing
When this check box is enabled (checked), the application includes parent entry's "print details" when printing linked children records. For example, you might have one or more embedded material lists within another list. If the parent list does not "print details" but another list linked to that parent is set to print details (true), the parameter (if checked) would override the parent's setting and print those details. If this check box is not enabled, the parent's "print details" setting is applied to any subsequent lists or details linked to it.
Custom Item Flags > Enable Custom Flags / Flag Heading
You can add inventory flags to item records to alert customers to hazardous materials that are part of the item's make up. When you select the Enable Custom Flags check box, and enter code characters in the Flag Heading field, the application adds the flag (when appropriate) to cash receipts, invoices, customer orders and quotes. Many businesses use this field to address local laws that require a receipt-level identification for hazardous materials sold to the public. Alternatively, you can use this flag for other purposes, such as for non-returnable items, to indicate a final sale, or to specify that the item is of US-origin, etc.
Unit Item Tally user defined fields
When you have unit item tally items enabled, you can a up to three user-defined text fields for item tracking. These fields then display in the Inventory Unit Item Maintenance form so you can describe the Supplier, Mill, and Location details associated with the Unit Tally Item. There is also an additional field for comments. You can learn more about this utility in the Inventory Unit Item Maintenance topic.
Label Preview Item
From this list, choose the template used to preview the label document when you create labels in theTags & LabelsDesign feature.
Label Preview Printer
From this list choose a valid printer for processing the label document for viewing. You must select an accessible printer for use of the preview feature available from the Label Designer.
Import from Catalog - Default Template Item
If the "Import from Catalog" feature is enabled for a branch location, the template you select from this list will be used as the default template when creating inventory items from the catalog import process. Creating a catalog entry does not mean the item exists in inventory.
Enable Qty Adjustments via Item Maintenance
Select this check box to enable authorized users to adjust item quantities from the Item Maintenance form.
Default GL Mapping for Qty Adjustments
Select the default GL account for item quantity adjustments in the Item Maintenance form. This selection is not required when the Enable Qty Adjustments via Item Maintenance check box is enabled.
Price Levels
Use these fields to establish up to seven pricing levels that your company will use for calculating item costs for specific groups of customers. Each price level must be assigned a Name description, a Grid Name (which is a shortened description used for grid display), a default calculation Type, and a percentage or amount (%/Amt) associated with the default calculation type value. The Type entry gives you pricing choices for each price level, including discounts off Suggested List, Markup or Margins using various costs, Set (or Fixed) pricing, and as Discounts off the Store Retail (the first level). The percentages or amounts associated with each price level (of discount, markup, margin, etc.) are set in the %Amt column. Amount entries are only used for Fixed Price type levels.
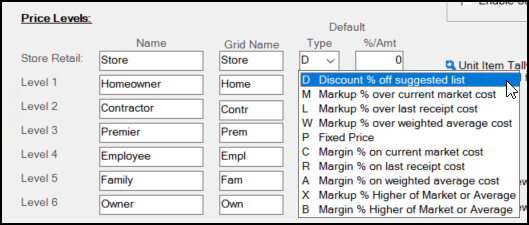
Pricing levels set here are the default pricing levels for the business. You can also set Branch Pricing, which is described in detail here. Price levels that are not completed won't be available for assignment to accounts.
The Store Retail is the only mandatory level. After these pricing levels are complete, you can assign a default price level to individual accounts.
"Grid Name" is a shortened version of the level's full name used for grid display (pricing selection from a grid area). There is less room in the drop-down selection panel for text descriptions, so we recommend shorter names for this purpose.
ABC Percent Rankings
An "ABC" report lists items based on and sorted by sales totals. Percentages are used to determine where the report stops to print totals. This could be used, for example, to produce sales totals for the items making up the top 10% of inventory, next 30%, and remaining 60%. A scheduled service runs monthly that classifies or ranks all inventory based upon sales. The ABC report is provided so that users can analyze their items using these rankings.
Users define the percentages for A, B, and C breaks. The three percentages must add up to 100%. Items ranked as A are the top percentage of your company's inventory, C is the lowest percentage, and B is the percentage of inventory between A and C. See the ABC Report to review the current product rankings for your inventory.
All inventory is ranked, regardless of whether the items have been sold or not. Some companies prefer to keep item records for goods they rarely or never stock whereas others only maintain item records for goods they actually maintain and sell regularly. For this reason, percentages will vary significantly by company.
How ABC Percentages WorkIf a company has a large inventory and most items have no sales history, it's best to set the A and B parameters to very small figures to get the best results. For example, if your inventory is large, let's say 50,000 items, but 10,000 of those goods are active, ranking the A, B, and C using percentages like 20, 30, and 50 respectively isn't going to do much. Why not? This is because all the active goods fall within the top 20% of the overall inventory. This causes the active portion of inventory to be reported entirely as "A" items while the B and C items become assigned to the remaining 80% (or 40,000 items). Using the same example, let's assume that we instead specified 5% for A, 5% for B, and 90% for C in our parameters. When monthly processing occurs, our 10,000 items would be ranked in a more usable fashion. The first 2,500 items with the highest sales would be assigned a rank of "A," the next 2,500 a rank of "B," and the remaining 5,000 active items would now be grouped under the "C" category (along with the 40,000 items with no activity). Companies that maintain smaller, more active inventories have far less to consider as far as ABC rankings as long as somewhere close to 100% of their inventory is actively used. It's always possible to tweak the percentages; however, changes only affect the next monthly ranking (this occurs once monthly only). |
Merge non-stocked items after N days sold
This parameter sets the number of days after an inactive generated item is sold that it will be merged back with its originating item. For an SO item to merge, either the "Last Sale Date" or the "Established Date" (for items that have never been sold) must be older than or equal to the date determined by this parameter. Merging takes time for each item, so we limit each daily merge to a maximum of 500 items. If you set the "After N Days Sold" value to "0", it will prevent the SO item from merging.
Merging is done automatically as a daily scheduled service. Non-stocked generated items will only purge if all quantities are zero (on-hand, on-order, committed, etc.) and as long as they are also not linked with any open documents. This prevents an item from being merged that has a stock value (due to a return for example) or is associated with an open transaction (purchase order, etc.). Some manual changes to a generated item's settings in Item Maintenance can potentially prevent the item from merging as well.
"Generated" items are created at time of processing after an "origin" item is used for initial entry on specific types of transactions (customer orders, work orders, purchase orders, etc.). The generated item is automatically assigned a unique SKU based upon the source transaction, document ID, and sequence. Item setting are based both on the source item and information required during entry (such as pricing, costs, and a description). The item type of a generated item is initially set to "renumbered" and after some level of processing to "resale."
The resulting items are used temporarily and are created when non-stocked items meeting certain criteria are processed with specific transactions.
The original (base) item must also have the following characteristics in Item Maintenance to be used for generating another item during processing:
•The item must be non-stocked (Stocked = N)
•The item must require a description (Description Reqd = Y)
•The item must NOT track on-hand quantities (Track Quantities On-hand = N)
•The item must NOT have any on-hand quantity.
Often these base items are used somewhat generically; however, it's usually best to use several different SKUs so that you can separately evaluate sales and other information after items are merged. Origin or base items may indicate a type of product (such as "SOFLOORING" or "SOWINDOWS," for example) or your company might prefer to create origin items which link to specific vendors.
In the case of a customer order, once a renumbered item has been ordered, received, and sold, the item is no longer necessary except perhaps for reference purposes or in case the customer returns the goods. This parameter sets the number of days these items should be retained before the sales history of the item is merged back into the origin item.