Customs Manifest
Customs Manifest provides the ability to record and submit import customs information in situations where goods are being imported internationally. The Customs Manifest is linked to purchase orders (POs) and can be used to create an XML file that is submitted to some government Customs departments using the Automated System for Customs Data (ASYCUDA), which is a United Nations (UN) based organization responsible for providing Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) services for International trade.
The Customs Manifest feature includes customs information, shipping information, ship-to information, container IDs associated with a manifest, a list of all vendor Purchase Orders (POs) with goods on the manifest, a combination of taxable and non-taxable adders based on item commodity codes, POs, and manifests, item-by-item commodity codes with associated duties and taxes, currency exchange between the vendor's and dealer's currency, reports, receiving of a manifest, and general ledger additions.
Depending on the products you purchase, you may owe a duty or tax. Nearly every shipment that crosses an international border is subject to the assessment of duties and taxes. Duties and Value Added Tax (VAT) are calculated as percentage of the customs value of the goods (item + insurance + shipping). Normally, duties and taxes on an international shipment will be billed directly to you by the global carrier.
While one manifest document relates to one "container" (i.e. shipping container), one manifest may be linked with one or more POs.
Please contact your aftermarket sales representative to enable this feature.
For instructions on how to create and print a Customs Manifest, click here.
Configuration
The first step in using the Customs Manifest feature is to turn the option on in Parameters, on the Setup/Software tab. This must be done by a Support team member. It is recommended that you restart the Spruce application after turning on the option. Once the feature is turned on, you must configure your settings at the branch levels. Additional defaults will need to be set in Vendor Maintenance and Item Maintenance as well.
Custom Manifest Settings in Branches
The Customs Manifest feature is configured at the Branch level in Maintenance > Database > Branches. Select the Branch ID and go to the Customs tab. The Customs tab will only be visible if the Customs Manifest option is turned on in Parameters. Once all settings have been entered press the Process (F12) option or the F12 function key on your keyboard to proceed.
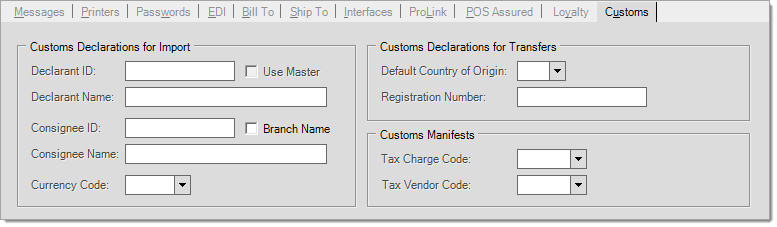
Customs Declarations for Import
-
Declarant ID / Name : Enter the Declarant ID and name in the designated fields. The declarant is the company (person) responsible for the import. The declarant must ensure the goods are legitimate, correctly valued and declared upon import.
-
Use Master: If this check box is selected, the Declarant ID and name will be the same as the master (main) branch.
-
Consignee ID / Name : Enter the ID number and name in the designated fields. This can be the same as the declarant information. The consignee is the entity who is financially responsible (the buyer) for the receipt of the shipment. In order to be recorded as the consignee on an import, a business must have a Consignee ID number.
-
Branch Name : If selected, the consignee name will be set to match the branch name.
-
Currency Code : Enter the currency your company generally uses for customs and duties. Currency codes are three (3) letter alphabetic codes that represent the various currencies used throughout the world.
Customs Declarations for Transfers
-
Default Country of Origin : The country from which you purchase the majority of your goods.
-
Registration Number : Importers and exporters are required to register with customs authorities for an importer or exporter Customs Registration Number. Enter registration number in this field.
Customs Manifests
-
Tax Charge Code : Select VAT (sales tax) or tax code to be used on AP invoices. This is defined is Point of Sale > Database > Sales Tax / VAT.
-
Tax Vendor Code : Select the tax vendor code to be used on AP invoices. This is defined is Point of Sale > Database > Sales Tax / VAT.
Customs Manifest Settings in Purchasing
Within Purchasing > Database > Customs Manifests, you will define the currency codes, office codes, status codes, and package codes to be used.
Currency Codes
Currency codes are three-letter alphabetic codes that represent the various currencies used throughout the world. From the Currency Code Maintenance form, you will define all the currency your company deals with. The conversion factors will need to be manually updated if rates fluctuate.
Enter the percentage values for:
•Customs : The government's tax on imports or exports.
•Costing : This is the value of your nation's currency versus the currency of another nation. For example, how many US dollars does it take to buy one Euro?
Office Codes
Enter the list of Office Codes you will be using to process your customs manifests. These office codes can include, but are not limited to, Customs Clearing Office, Loading Office, Location of Goods, Bank Codes, Bank Payment Terms, Port of Arrival, Port of Departure, Warehouse, Port of Authority, etc. To create a new line item, select a blank field and enter the desired information in that list. The list should be comprised of all customs agencies you will be dealing with, banks, warehouse, etc. Select the "Disable" option if a code becomes obsolete at any point.
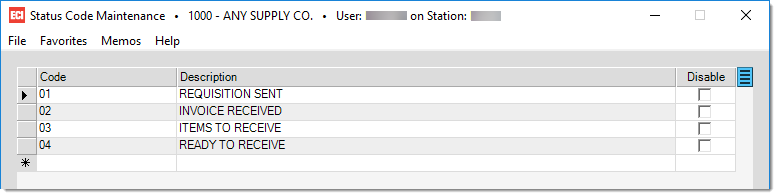
Status Codes
Status codes are not required or viewed by the government/customs. Status codes are used for your company's own tracking purposes. To create a new code, select an empty row and enter the code and a description. Select the "Disable" option if a code becomes obsolete at any point. In our example below, the status codes are used to track the various shipment statuses. Press F12 Process to save your changes.
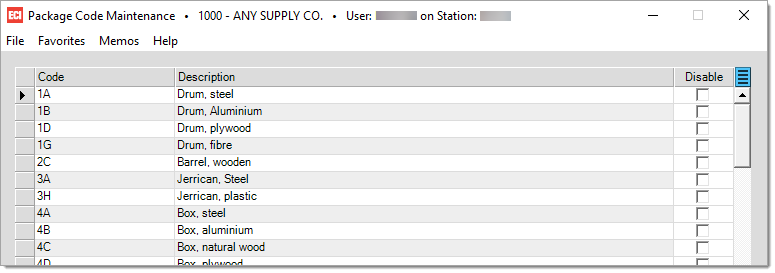
Package Codes
Package Codes are provided by ASYCUDA (or other governmental agency) and must be present on customs manifest documents. To enter a new code, select an empty row and enter the code and description provided by ASYCUDA (or other government standard your country follows). Select the "Disable" option if a code becomes obsolete at any point. Press F12 Process to save your changes.
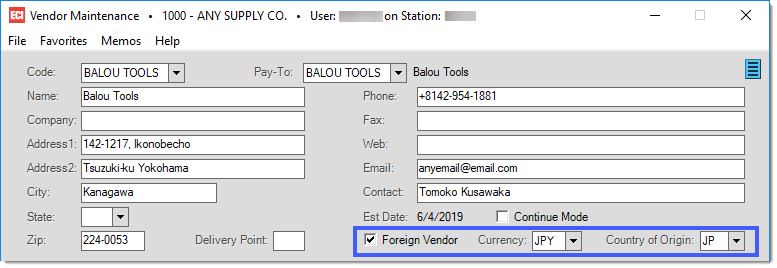
Custom Manifest Settings in Vendor Maintenance
Once the Branch settings and various codes have been defined, navigate to Vendor Maintenance in Purchasing > Database. If the Customs Manifest option is turned on, three (3) new options will be visible on the Vendor Maintenance form: Foreign Vendor, Currency, and Country of Origin. By selecting the Foreign Vendor option, you are indicating that purchases from this vendor are made through the customs manifest feature. The Currency field is the currency the vendor deals in. If a vendor deals in multiple currencies, you would setup multiple vendors with a different currency. The Country of Origin defines where the product is from.
Customer Manifest Settings in Item Maintenance
When using customs manifest, products are not taxed based on the item, but rather on the commodity code set on the Common/Codes tabs. Commodity codes are required for manifest processing. These can be added at time of ordering. If added at time of ordering and the item has no existing commodity code, the code will be automatically associated with the item. Commodity codes can be overridden on a Purchase Order. Special circumstances may alter the tax rules for a particular type of commodity.
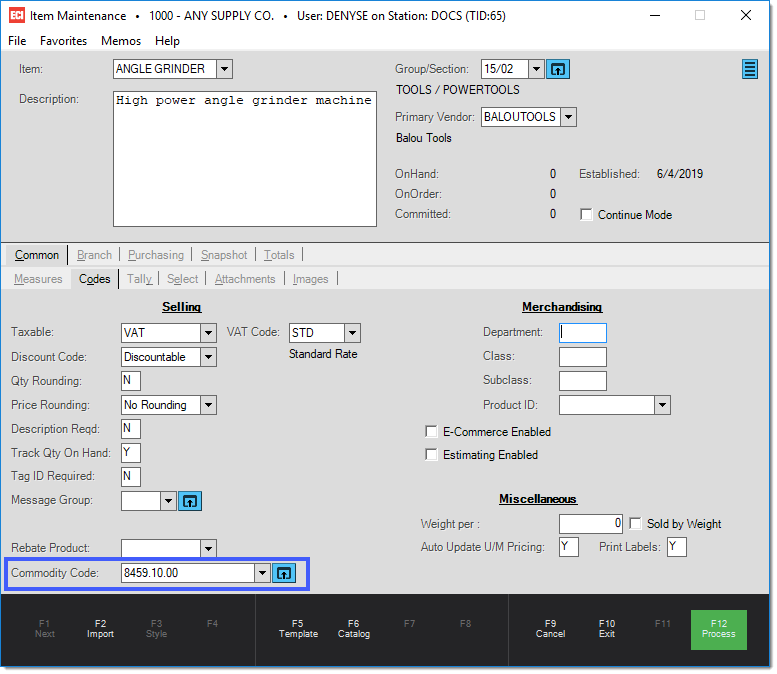
Commodity codes, also known as tariff commodity codes, are used to classify any goods being imported or exported. It is important to use the correct commodity code(s) to ensure compliance with customs declarations, and pay the right taxes and duties. Any separators in commodity codes are removed when submitting data to ASYCUDA. You can use separators to create unique codes that have the same numeric value but may have different tax structure. For example, the same code may be taxable in one situation, but not another. You can setup to different codes with the same numeric value to solve this situation (1234.56.78 and 1234*56*78 are equivalent). You may want to come up with some type of rules or procedure for how you use separators.
Use the Commodity Code field to select or enter an existing commodity code, or click on the Settings icon ![]() by the Commodity Code field. From the Manifest Commodity Codes form, you can select an existing commodity code or create a new one by typing the code in the Commodity Code field. You may either enter the code description attached to the commodity code as assigned by your customs agency or enter your own description; customs agents will typically look at the commodity codes, not the description. The Unit for Duty defines how the taxes will be applied (each, pkg, etc.). The columns in the data grid reflect the values entered in the Customs Tax Code Maintenance form; it is possible to modify the values if needed. For each tax calculation listed in the grid, you may include or exclude other tax calculations by listing them in the designated column.
by the Commodity Code field. From the Manifest Commodity Codes form, you can select an existing commodity code or create a new one by typing the code in the Commodity Code field. You may either enter the code description attached to the commodity code as assigned by your customs agency or enter your own description; customs agents will typically look at the commodity codes, not the description. The Unit for Duty defines how the taxes will be applied (each, pkg, etc.). The columns in the data grid reflect the values entered in the Customs Tax Code Maintenance form; it is possible to modify the values if needed. For each tax calculation listed in the grid, you may include or exclude other tax calculations by listing them in the designated column.
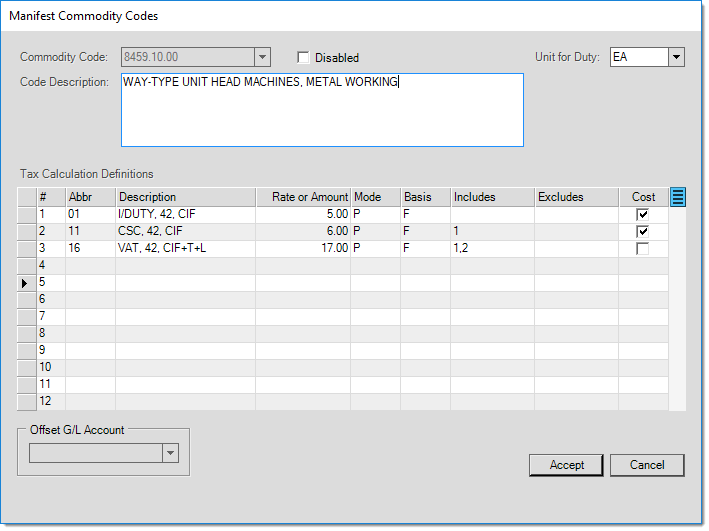
Each Commodity Code can have one or multiple tax calculations attached to it. These tax calculations are defined in the Customs Tax Code Maintenance form. To access the Customs Tax Code Maintenance box, choose the data grid's Menu Marker ![]() and select Add/Edit Tax Code.
and select Add/Edit Tax Code.
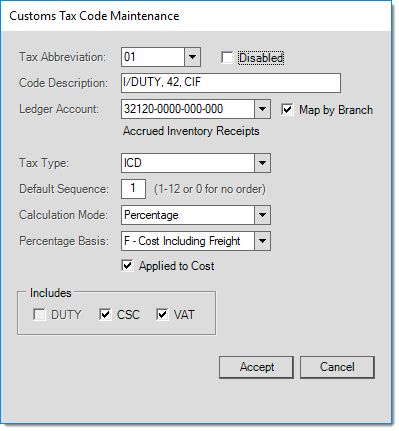
To create a new Tax code, enter the new tax abbreviation in the “Tax Abbreviation” field. Press the Accept button once all defaults have been selected.
Tax Abbreviation : Enter the tax abbreviation.
Code Description: The description of the tax code.
Ledger Account: Link a tax code to a general ledger account.
Tax Type: Select the tax type from the drop-down list. This information is used by ASYCUDA to identify the tax type applied to the goods. Verify with your governing agency for the tax codes used by your country. Click here for an example of Tax Types.
* The above is an example of tax codes (types). Consult with your governing agency the list of tax codes for your country. |
Default Sequence: Determines where this particular tax code will be displayed in the data grid on the Manifest Commodity Code form. This allows for an easy visual indication of the taxation scheme for the item, for example users know that line 1 is always duty and line 3 is always the VAT tax. A value of zero (0) indicates that no specific order is required for the tax codes.
Calculation Mode: Select whether the tax is calculated as a percentage, flat, quantity unit, weight unit or volume unit rate. Selecting the Unknown option means that you are manually selecting this value every time the item is selected.
Percentage Basis: Select whether the percentage is applied to the Cost Only, Cost including Freight. Selecting the Unknown option means that you are manually selecting this value every time the item is selected.
Applied to Cost: Determines whether the tax is applied to the delivered cost calculations of the items in the Purchase Order.
DUTY/CSC/VAT: Select any additional taxes to apply to the tax code.